Bunions Cause And Effect
Overview
 A bunion is a bone deformity caused by an enlargement of the joint at the base and side of the big toe ( metatarsophalangeal joint ). Bunions form when the toe moves out of place. The enlargement and its protuberance cause friction and pressure as they rub against footwear. The growing enlargement or protuberance then causes more irritation or inflammation. In some cases, the big toe moves toward the second toe and rotates or twists, which is known as Hallux Abducto Valgus. Bunions can also lead to other toe deformities, such as hammertoe.
A bunion is a bone deformity caused by an enlargement of the joint at the base and side of the big toe ( metatarsophalangeal joint ). Bunions form when the toe moves out of place. The enlargement and its protuberance cause friction and pressure as they rub against footwear. The growing enlargement or protuberance then causes more irritation or inflammation. In some cases, the big toe moves toward the second toe and rotates or twists, which is known as Hallux Abducto Valgus. Bunions can also lead to other toe deformities, such as hammertoe.
Causes
With prolonged wearing of constraining footwear your toes will adapt to the new position and lead to the deformity we know as a foot bunion. Footwear is not the only cause of a bunion. Injuries to the foot can also be a factor in developing a bunion. Poor foot arch control leading to flat feet or foot overpronation does make you biomechanically susceptible to foot bunions. A family history of bunions also increases your likelihood of developing bunions. Many people who have a bunion have a combination of factors that makes them susceptible to having this condition. For example, if you are a women over the age of forty with a family history of bunions, and often wear high-heeled shoes, you would be considered highly likely to develop a bunion.
Symptoms
The dominant symptom of a bunion is a big bulging bump on the inside of the base of the big toe. Other symptoms include swelling, soreness and redness around the big toe joint, a tough callus at the bottom of the big toe and persistent or intermittent pain.
Diagnosis
A doctor can very often diagnose a bunion by looking at it. A foot x-ray can show an abnormal angle between the big toe and the foot. In some cases, arthritis may also be seen.
Non Surgical Treatment
Detecting and treating bunions can relieve many of the symptoms associated with this condition. Doctors often consider whether the condition requires non-surgical or surgical treatment. The decision is based on the severity of the symptoms. Because bunions often get worse over time, early detection and proper treatment are very important. Some non-surgical methods to reduce the symptoms related to bunions include cushioning the area with padding or tape, taking medication to relieve pain and inflammation, using physiotherapy to reduce pain and related symptoms (e.g., ultrasound, whirlpool baths, joint mobilization), wearing custom orthotics to provide better movement and stability of the foot, wearing well-fitted comfortable shoes that are not too tight (if your shoes used to fit but now are too tight around the bunion area, you may be able to have them stretched in this area), using a special splint at night to decrease the amount the toe angles towards the other toes. When non-surgical methods do not provide relief, surgery may be needed. During surgery, the doctor will remove the tissue or bone in the area of the bunion and attempt to straighten the big toe, and may join the bones of the affected joint. 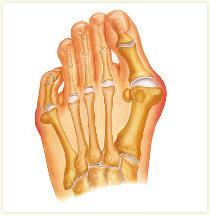
Surgical Treatment
Bunion surgery is occasionally required when the bunion deformity is too advanced for conservative treatment to work. Your surgeon will usually cut an angular section from the bone to correct the alignment. In some cases, multiple toes may need to be straighten.
Prevention
Here are some tips to help you prevent bunions. Wear shoes that fit well. Use custom orthotic devices. Avoid shoes with small toe boxes and high heels. Exercise daily to keep the muscles of your feet and legs strong and healthy. Follow your doctor?s treatment and recovery instructions thoroughly. Unfortunately, if you suffer from bunions due to genetics, there may be nothing you can do to prevent them from occurring. Talk with your doctor about additional prevention steps you can take, especially if you are prone to them.